装置运行原理详解。
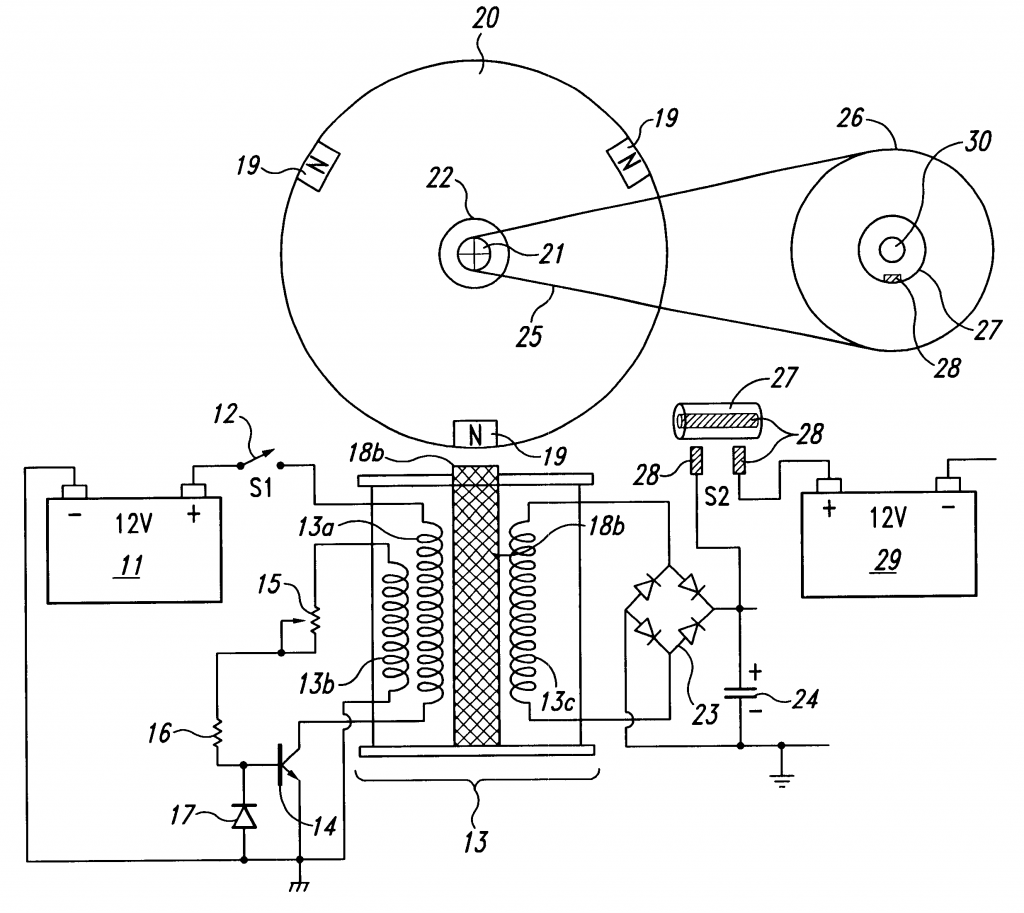
First, the switch 12 is closed. Because the transistor 14 is off, no current flows through the winding 13a.
首先,开关 12 被关闭,因为三极管 14 是没有导通的,没有电流流过线圈13a。
Next, the motor is started by rotating the rotor 20, say, in a clockwise direction. The rotor may be rotated by hand, or by a conventional motor-starting device or circuit (not shown).
下一步,电机可以通过旋转转子20启动,假设在一个顺时针方向的方向。转子可以用手使其旋转,或藉着一个传统的启动电动机设备或电路。 (不显示)。
As the rotor 20 rotates, the pole 19 moves from the three o'clock position towards the pole piece 18b and generates a magnetic flux in the windings 13a,13b and13c. More specifically, the stator 18a and the pole piece 18b include a ferromagnetic material such as iron. Therefore, as the pole 19 moves nearer to the pole piece 18b, it magnetises the pole piece 18b to a polarity – South in this instance – that is opposite to the polarity of the pole 19 (which is North). This magnetisation of the pole piece 18b generates a magnetic flux in the windings 13a-13c. Furthermore, this magnetisation also causes a magnetic attraction between the pole 19 and the pole piece 18b. This attraction pulls the pole 19 toward the pole piece 18b, and thus reinforces the rotation of the rotor 20.
如果转子 20 旋转,磁极19 从三点钟位置移动向线圈铁芯18b ,而且在线圈 13 a、13 b 和 13 c中产生磁流。更具体的,定子18a和磁芯18b由铁磁材料组成,例如铁。因此,当磁极19靠近18b,它磁化18b变成南极,与磁极19(北极)的磁极相反。18b磁化在线圈13a—13c中产生磁流。进一步,磁化引起一个吸力。吸力拉动磁极19向18b移动,因此增强了转子20的旋转。
The magnetic flux in the windings 13a-13c generates voltages across their respective windings. More specifically, as the pole 19 rotates toward the pole piece 18b, the magnetisation of the stator 18a and the pole piece 18b, and thus the magnetic flux in the windings 13a-13c, increases. This increasing flux generates voltages across the windings 13a-13c such that the dotted (top) end of each winding is more positive than the opposite end. These voltages are proportional to the rate at which the magnetic flux is increasing, and so, they are proportional to the velocity of the pole 19.
在线圈13a-13c中各自产生电压。线圈上面的点比下面的更多正极性。这些电压与磁束增加的速率成比例关系,因此,他们与19 的速度成比例.
At some point, the voltage across the winding 13b becomes high enough to turn the transistor 14c on. This turn- on, i.e., trigger, voltage depends on the combined serial resistance of the potentiometer 15 and the resistor 16. The higher this combined resistance, the higher the trigger voltage, and vice-versa. Therefore, one can set the level of the trigger voltage by adjusting the potentiometer 15.
在某一时刻, 13 b 电压足够高使三极管 14 c 的导通。触发电压由电阻15和16决定,15和16的电阻越高,触发电压越高。因此,触发电压能藉由调整电位器 15 设定。
In addition, depending on the level of voltage across the capacitor 24, the voltage across the winding 13c may be high enough to cause an energy recovery current to flow through the winding 13c, the rectifier 23, and the capacitor 24. Thus, when the recovery current flows, the winding 13c is converting magnetic energy from the rotating pole 19 into electrical energy, which is stored in the capacitor 24.
此外,根据电容器 24 的两端电压,线圈 13 c 两端的电压要足够高才能产生一个恢复电流通过整流器 23到电容器24.因此,当恢复电流发生,线圈 13 c 正在使旋转极 19的磁能转化为电能储存到电容器24.
Once turned on, the transistor 14 generates an opposing magnetic flux in the windings 13a-13c. More specifically, the transistor 14 draws a current from the battery 11, through the switch 12 and the winding 13b. This current increases and generates an increasing magnetic flux that opposes the flux generated by the rotating pole 19.
一旦三极管导通,在线圈13a-13c中产生反向的磁流。更具体而言,三极管从电池11中抽取一个电流,通过开关12和线圈13b。这个电流增长并产生一个增长的磁流且与转子产生的磁流相反。
When the opposing magnetic flux exceeds the flux generated by the rotating pole 19, the opposing flux reinforces the rotation of the rotor 20. Specifically, when the opposing flux (which is generated by the increasing current through winding 13a) exceeds the flux generated by the pole 19, the magnetisation of the pole piece 18 inverts to North pole. Therefore, the reverse-magnetic pole piece 18 repels the pole 19, and thus imparts a rotating force to the rotor 20. The pole piece 18 rotates the rotor 20 with maximum efficiency if the pole-piece magnetisation inverts to North when the centre of the pole 19 is aligned with the centre of the pole piece. Typically, the potentiometer 15 is adjusted to set the trigger voltage of the transistor 14 at a level which attains or approximates to this maximum efficiency.
当反向磁流超过转子产生的磁流,反向磁流增强转子旋转。具体地,当13a的反向磁流超过转子产生的,磁芯18变成N极,所以,18排斥19,赋予转子20一个旋转力。当19中心与18中心对齐的时候18驱动20效率最高。通常,调节电位器15来设置触发电压以达到效率最高。
The transistor 14 then turns off before the opposing flux can work against the rotation of the rotor 20. Specifically, if the pole piece 18 remains magnetised to North pole, it will repel the next pole 19 in a direction (counterclockwise in this example) opposite to the rotational direction of the rotor 20. Therefore, the motor turns transistor 14 off, and thus demagnetises the pole piece 18, before this undesirable repulsion occurs. More specifically, when the opposing flux exceeds the flux generated by the pole 19, the voltage across the winding 13b reverses polarity such that the dotted end is less positive than the opposite end. The voltage across the winding 13b decreases as the opposing flux increases. At some point, the voltage at the base of the transistor decreases to a level that turns transistor 14 off. This turn-off point depends on the combined resistance of potentiometer 15 and resistor 16 and the capacitance (not shown) at the transistor base. Therefore, potentiometer 15 can be adjusted, or other conventional techniques can be used to adjust the timing of this turn-off point.
在反向磁通抑制转子20旋转之前,三极管 14 关闭。明确地,如果磁芯18保持磁化为北极,它将会反对下一个单极19转过来。因此,电动机关掉三极管 14,18从而消磁, 在这个不受欢迎的斥力发生之前。更明确,当反向磁通超过被极 19 发生的磁通, 线圈13 b两端的电压颠倒极性,以致于有点的端比反向的端更少的正极性。当做反向磁通增大线圈 13 b 两端电压减少。另一点,三极管基极的电压减少到一定水平后三极管 14关闭。这关闭点取决于电位器15 和电阻 16 的组合电阻和在三极管基极电容容量(不显示)。因此,电位器15 能被调整,或其他传统的技术能被用来调整这关闭点的正时。
The rectifier 23 and capacitor 24 recapture the energy that is released by the magnetic field (which energy would otherwise be lost) when the transistor 14 turns off. Specifically, turning transistor 14 off abruptly, cuts off the current flowing through winding 13a. This generates voltage spikes across the windings 13a-13c where the dotted ends are less positive than their respective opposite ends. These voltage spikes represent the energy released as the current-induced magnetisation of stator 18a and pole piece 18b collapses, and may have a magnitude of several hundred volts. But, as the voltage spike across the winding 13c increases above the sum of the two diode drops of the rectifier 23, it causes an energy-recovery current to flow through the rectifier 23 and the voltage across the capacitor 24 charge the capacitor 24. Thus, a significant portion of the energy released upon collapse of the current-induced magnetic field is recaptured and stored as a voltage in the capacitor 24. In addition, the diode 17 prevents damage to the transistor 14 by clamping the reverse base-emitter voltage caused by the voltage spike across the winding 13b.
当三极管 14 关掉时,整流器 23 和电容24 俘获被磁场释放的能量。明确地,突然地关掉三极管 14,切断流过线圈 13a的电流。将产生电压尖峰在线圈 13 a-13c。这些电压尖峰表明当由电流引起的 18 a和18 b磁场突然崩溃,而且可能有数百电压的大小。但是,当在13 c的电压尖峰 增大到高于整流器 23 的二极管电压, 能量回收电流通过整流储存到电容24中.因此,在电流引起的磁场的突然崩溃之后被释放的能量的重要部分储存在电容24。此外,二极管 17保护三极管 14 免受13b的伤害。
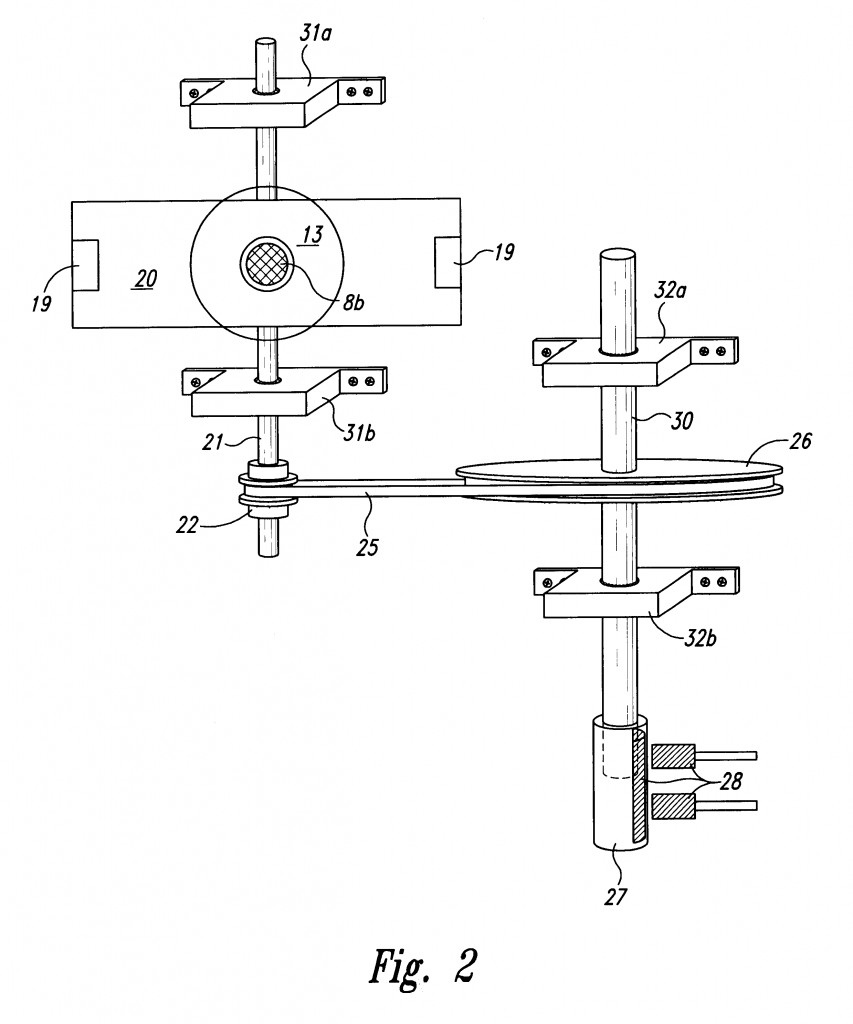
The recaptured energy can be used in a number of ways. For example, the energy can be used to charge a battery 29. In one embodiment, the timing wheel 26 makes two revolutions for each revolution of the rotor 20. The contact rotor 27 closes a switch 28, and thus dumps the charge on the capacitor 24 into the battery 29, once each revolution of the wheel 26. Other energy-recapture devices and techniques may also be used. Rotor 20 may be stopped, either by applying a brake to it or by opening the switch 12.
捕获的能量可以有多种使用方式。例如,能用来给电池29充电。其中一个实施方法中,转子20旋转1次定时轮26旋转2次。连接器27关闭开关28,把电容24的电荷泵浦到电池29中,轮子26每旋转一次发生一次。其他能量俘获设备和技术也可以使用。转子20可以被停止,不管是通过施加一个制动还是打开开关12.
Other embodiments of the monopole motor are contemplated. For example, instead of remaining closed for the entire operation of the motor, the switch 12 may be a conventional optical switch or a Hall-effect switch that opens and closes automatically at the appropriate times. To increase the power of the motor, the number of stators 18a and pole pieces 18b, may be increased and/or the number of poles 19. Furthermore, one can magnetise the stator 18a and pole piece 18b during the attraction of the pole 19 instead of or in addition to magnetising the stator and pole piece during the repulsion of the pole 19.
单极电机的另外实施,例如,开关12可以被光控开关或者霍尔开关打开和关闭。为了增加电机的能量,可以增加18a的数量或者19的数量。进一步,可以在19吸引18b的阶段磁化定子18a代替19排斥定子的时候磁化定子(也就是吸力模式)。
Moreover, the stator 18a may be omitted so that coil 13 becomes an air coil, or the stator 18a and the pole piece 18b may compose a permanent magnet. In addition, although the transistor 14 is described as being a bipolar transistor, a MOSFET transistor may also be used. Furthermore, the recaptured energy may be used to recharge the battery 11. In addition, although described as rotating in a clockwise direction, the rotor 20 can rotate in a counterclockwise direction. Moreover, although described as attracting a rotor pole 19 when no current flows through winding 13a and repelling the pole 19 when a current flows through winding 13a, the pole piece 18b may be constructed so that it attracts the pole 19 when a current flows through winding 13a and repels the pole 19 when no current flows through winding 13a.
此外,定子18a可以省去以至于13变成了一个空心线圈,或者可以用永磁组成。另外,尽管三极管14被描述成一个双极晶体管,一个MOSFET晶体管也可以使用。而且,回收能量可以被用于给电池11充电。尽管转子描述为顺时针旋转,也可以是逆时针旋转。尽管当没有电流流经线圈13a时吸引转子19,当有电流流经13a时排斥19,实际也可以安排为有电流时吸引,无电流时排斥。